- Home
- QA Sherpa
- Blog & News
- Embedded Quality
Tag: Embedded Quality
Too Busy for User Acceptance Testing (UAT)?
- October 24, 2024
- Kevin Rutkowski
- Comments Off on Too Busy for User Acceptance Testing (UAT)?

I Love UAT
One of my favorite parts of testing is getting the opportunity to coordinate UAT. I love it because we’re getting feedback from the people who are actually going to use the system once it goes live. Even if a team is great about getting user input, everything up to this point is theoretical. All of us can think we know what we want, but once we actually see it, touch it, and live with it, we don’t know if what we asked for is what we really wanted or needed.
I’m planning to write a few articles about what I’ve learned during my UAT experiences, and I hope it will help others with their efforts.
Who Should Perform UAT?
The obvious answer to who should perform UAT is “users”. What users should perform UAT, though? Like many things, “it depends.” For a public-facing application, you may want people from the general public who don’t have a lot of deep knowledge about the system or industry. For an internal application, you likely want experienced users. However, those experienced users will often, understandably, plead that they are “too busy” to help test.
At one of my past clients, I requested the time of experienced users to test a back-end system for processing college applications. Like most companies, they were a bit understaffed and perpetually a bit behind at getting the work done. To the team, and to the manager who was trying to guard their time, my request was just one more bit of unnecessary busywork added to their plate.
The manager offered to hire a temporary worker to perform UAT so their most experienced workers wouldn’t be pulled away from their important work.
The Users Will Live with the Results
Given what I’ve seen others do with UAT in the past, this team may have believed that UAT was simply going to be formality where they would run tests that I had already verified met the written requirements. UAT is sometimes simply a step done to mark a checkbox in the few days before going live. However, when I run a UAT effort, it is much more than that.
I knew that having a temp worker wouldn’t give our team the insight we needed. A temp worker could certainly execute a pre-written test script, but that is not a useful way to perform UAT in my experience. Our team needed to know if this software truly met the needs of the team. We genuinely wanted to know, and we planned to incorporate the feedback into the final product.
I had a heart-to-heart with the manager and the team lead. I explained to them that their team would be using this application to do all of their work in the not-too-distant future. The team, in order to make the most of their investment, would likely be using the software for years. Shortly after the software went live, I’d be gone, but their team would be living with the results.
I explained that we truly were going to take their input into account to ensure the best software for doing their work. Then I asked if they still wanted a temp to be responsible for giving that input and making those decisions that would affect their team for years.
Once they understood the true impact of UAT, the answer was obvious. The manager and lead both made time for UAT, and they even had another employee participate. They brought on a temporary worker to handle some of the more routine clerical tasks instead of having them perform UAT.
We did incorporate their feedback into the final product, and the client was very happy with the end product. It was a true improvement to their old system.
If you could use some guidance with user acceptance testing, please reach out to me at kevin@qasherpa.com

Those Pesky Bugs – Special Characters
- July 18, 2024
- Kevin Rutkowski
- Comments Off on Those Pesky Bugs – Special Characters
Pesky Bugs
Some bugs keep popping up in project after project. It’s important to catch these sneaky bugs before they get into a production system.
In the past, in a one month period, I caught three separate bugs that occurred due to improper handling of special characters. This type of bug can be easily missed if the test team isn’t specifically looking for it.

Culprit 1 – <
The innocent less-than sign is usually used for good. However, it can be a menace when it falls into the wrong hands. It can be used to send malicious executable scripts into systems from web pages.
Our program screened out HTML characters from the main entry screen by design. So, we didn’t expect to have any problems. However, it turned out that a portion of data in the system was imported from a spreadsheet rather than entered through the data screens. When the user tried to use a feature that created a new record from an existing record, the system failed. With a little digging and changing the settings that determine how the error messages are displayed, we identified the error.
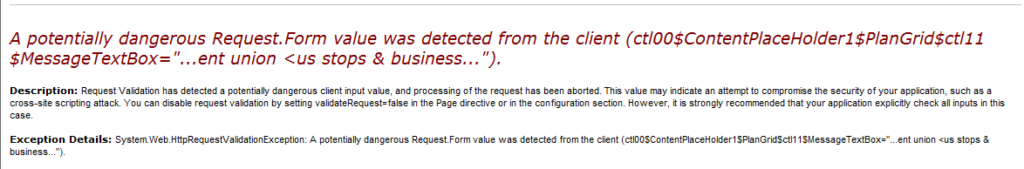
Of course, this brings up an additional issue of how to handle data imports to screen out data that would fail the validation rules, but that’s a discussion for another time.
Culprit 2 – ñ
Of course, any site that accepts names should be sure to accept the letter ñ. In my experience, this letter typically hasn’t caused a problem, but it did cause a problem on a recent project. We built a system where people could set up a secure profile that included their name. The name and some other information were then sent to a third party that would send a welcome e-mail. Because we utilized Embedded Quality, we tested profile creation early, which included testing names containing ñ. Everything worked fine early on.
In a later round of testing, the ñ started causing an error. As we dug into the problem, we found that the issue was that the 3rd party e-mail system could not understand the Unicode representation of ñ. Instead, the 3rd party expected this character to be in UTF format. Once we realized that, we were able to convert the format of the characters before sending them to the e-mail vendor.
Culprit 3 – : )

On the same project, we encountered an error that became known as the “smiley face” bug. This bug was not found until user acceptance testing, which is much later than I like to find bugs. In this case, we had tested online profile IDs that contained every acceptable special character without a problem. However, we did not specifically test the situation where the profile ID ended with a smiley face emoticon. When one user created an ID of janed:), the profile creation failed.
It turned out that the expression in code that checked for a duplicate profile ID before creation could handle any special character except for a single, right parenthesis. It interpreted that character as part of the expression, and caused a failure.
Summary
Encountering these 3 special character errors within a one month period reminded me of how important it is to test for every special character before going live. The experience validated my general rule of “if the system allows it, the users will do it.”
Have any of you found bugs due to special characters? Have any made it into production? If so, what was the consequence?
Embedded Quality – Development Team
- November 29, 2022
- Kevin Rutkowski
- Comments Off on Embedded Quality – Development Team
When I’ve introduced Embedded Quality to the developers on a project, a common reaction is fear and loathing. They often have a visceral, negative reaction to the words “Quality Assurance,” and the idea of working more closely with the Quality Assurance team instills a feeling of dread in them.

As a reminder, I originally outlined the basic concepts of Embedded Quality in this blog post. The concepts are:
- Quality Assurance starts on Day 1
- Quality Assurance is part of the Core Project Team
- Quality Assurance is performed by qualified experts
- General User Acceptance Testing does not begin until Core Project Team QA is complete
- Strong Foundation – No code is “Complete” until it is tested and works correctly
Although the developers I’ve worked with generally have a negative first reaction to the concept of Embedded Quality, once they’ve experienced it, they almost always request it on their next project. The question is, “how can we convince developers to try Embedded Quality the first time?”
Overcoming Common Concerns
I’ve found that it’s typically harder to overcome the developers’ concerns than the Quality Assurance team’s concerns because the developers usually start with the mindset that they don’t want to use Embedded Quality. However, there are ways to address their concerns.
The Code Isn’t Ready to Test
The developers will often say that the code really isn’t ready to test until very close to the end of the project. However, there are some good reasons why this should not be the case.
- The project schedule generally shows sections of code being completed before the end of the project. If a developer says that the code is complete, it’s difficult to imagine why it can’t be tested.
- It’s much easier to identify and fix bugs in small portions of code.
- Finding and fixing bugs early means that new code is built on a solid foundation.

Having the Quality Assurance team test code early in the process is analogous to having a building inspector view various portions of a building before it is complete. It makes a lot of sense for the inspector to check the foundation, the electrical, the plumbing, and the HVAC system before the building is anywhere near complete. Fixing these items after the building is complete is much more costly and difficult than fixing them earlier.
It Will Take Too Much of My Time
Another concern that developers have is that they will have to spend too much time explaining things to the testers. Because the code isn’t complete, they are afraid that the testers will report bugs for items that are simply not yet finished. Also, they will have to spend more time explaining how to test certain items when the complete UI may not be available.
These concerns are legitimate and show the need for having a test team of qualified experts. The testers should have a mindset of collaboration with the developers rather than antagonism. The testers will work closely with the developers to understand what code can be tested and what code is not ready. Of course, any code that is not ready cannot be considered complete for project planning purposes.
It is also true that the developer will have to spend more time explaining how to test some incomplete code. However, if the Quality Assurance team is qualified and experienced, they should be able to quickly learn any tools needed for testing. In my experience, any extra time that the developers spend helping the Quality Assurance team is saved many times over by finding the problems early.
I Don’t Need the Extra Pressure of Someone Looking Over My Shoulder
Many developers have had bad experiences working with testers who take delight in pointing out the flaws of others. These types of testers tend to make comments like, “I don’t know what those developers were thinking,” when they chat with each other in the break-room. This attitude really does put unnecessary pressure on the developers and contributes to a hostile relationship between developers and testers.

This is why it’s critical to ensure that the Quality Assurance team is made up of true professionals. I always remind the developers that Quality Assurance is part of the core team, which means that our goal is to ensure that the project gives a good impression to everyone outside of the team. I tell the developers that I know that they’re good developers and that bugs are a normal part of the process. The developers shouldn’t feel bad if the Quality Assurance team finds bugs. In fact, they should be happy because every bug that is found by the Quality Assurance team is one not found by the project sponsor or the end users. The project sponsor and the end users are the people who are generally the harshest critics of the development team.
Other Concerns?
I’d like to know what concerns you would have introducing Embedded Quality into your organization. What concerns would you anticipate from others? I’ll do my best to address those concerns in future posts.
Offshore Agile Testing…a Request from Management
- December 8, 2017
- Kevin Rutkowski
- Comments Off on Offshore Agile Testing…a Request from Management
A friend of mine asked me for some advice about how to run an Agile software development team with the developers and business users working in the US and the testers working for an outsourcing company in India.
My short answer was, “You can’t”.
The Agile Manifesto and Offshore Testing
I’ve actually had similar requests a number of times over the past few years. Managers want to be “Agile” and want to use “Offshore resources” so they ask their project teams to implement the combination of the two hot concepts. In the cases that I’ve seen, management has tried to send only the testing portion of development offshore. They wanted the onshore, local team to be “Agile”, but they also want to send code “over the wall” to an offshore test team. Unfortunately, these two concepts do not work together.
The Agile Manifesto principles include “Business people and developers must work together daily throughout the project;” “Build projects around motivated individuals. Give them the environment and support they need, and trust them to get the job done;” “The most efficient and effective method of conveying information to and within a development team is face-to-face conversation;” and “The best architectures, requirements, and designs emerge from self-organizing teams.”
These 4 (out of 12) principles are very difficult, if not impossible, to implement in an environment where the testers are separated from the rest of the team by geography and time zones. In addition, when only the test team is outsourced to another company, the testers often are required to communicate with the rest of the team via a single point of contact rather than directly with developers and business people.
To make things even more difficult, I’ve found that offshore, outsourced teams are typically set up to run a full, lengthy regression test for each build. In one case, I worked with a team that was trying to do Agile development with a test team that insisted on running a 6 week regression test for every build. This ran completely counter to the Agile Manifesto principle of “Deliver working software frequently, from a couple of weeks to a couple of months, with a preference to the shorter timescale.”
Can Agile Work with Offshore Teams?
I believe that Agile development can work with offshore teams if the teams are structured correctly and significant effort is put forth in building trust. Here are some techniques that I’ve used effectively to help build an Agile, globally distributed team.
- Have a full team consisting of all roles in each geographic location. This means that developers, testers, and business experts must be physically located in each location. The business expert may be a Product Owner Advocate rather than the actual Product Owner.
- Ensure that everyone on the global team has time to work together in person early in the project. This means flying people around the world which can be costly, but it makes a huge difference in the ability for team members to trust each other and work together.
- If the team is divided into drastically different time zones, schedule specific weeks throughout the project where the global team will work at the same time regardless of time zone. During these weeks, the team should make a concerted effort to communicate in real time with their counterparts around the world.

In a future post, I’ll talk about some additional techniques that are not specific to Agile that I’ve used to make global teams more effective.
Further Reading
Over the years, I’ve found these articles helpful in understanding the issues related to Agile distributed teams and how to address those issues. Maybe you’ll find them useful as well. To me, the two articles available for purchase from IEEE Computer Society were definitely worth the small cost.
Agile Strategies for Geographically Distributed Teams
Global Development and Delivery in Practice
Agile Offshore Techniques – A Case Study (Available for purchase)
Using and Agile Software Process with Offshore Development
Follow the Sun: Distributed Extreme Programming Development (Available for purchase)
Your Experiences
I’d like to hear any of your experiences with global Agile software development. What worked and what didn’t?
Contact me if you’d like help improving the effectiveness of your global team.
Drama Addiction
- November 14, 2016
- Kevin Rutkowski
- Comments Off on Drama Addiction
In a previous post, I lamented people who were rewarded for heroic efforts despite their earlier actions causing the problems in the first place.
A couple of people commented that these “heroes” usually didn’t intentionally cause the near-disaster situation. More often, they caused the situation by neglecting to follow a proven process or by simply not being proactive. I agree with these comments, and I believe that this points to a common problem. People tend to celebrate the visible, novel, and dramatic rather than the smaller, more important actions that keep things running smoothly.
Visible, Novel, and Dramatic
When I spoke at Agile Austin a number of years ago, one of the panelists mentioned that his team’s agile processes were working smoothly and his team was more productive than ever. However, several of his team members were becoming bored and unmotivated because everything ran too smoothly.
Around the same time, a friend on Facebook expressed frustration with the fact that people who lose weight “can brag about weight loss and exercise regimens and get praised by all, but a person talks about her workout and expresses pride, and they are met with sarcasm or daggers.”

This made me realize that people are rewarded more for the visible, novel, and dramatic in many areas of life beyond software projects.
- Politicians rarely brag about money spent on maintaining existing roads and bridges; however, they’re quick to take credit for new roads and bridges.
- A new, entry-level employee can impress co-workers by showing up on time and performing basic tasks competently; however, excellent performance is simply expected from a 15-year veteran employee.
- The first responders to a terrorist attack are celebrated as heroes, but the multitudes of people who worked to prevent many other attacks live in anonymity.
- A pilot who safely lands a plane with mechanical trouble is revered, but the pilots and other people who ensure thousands of safe flights per day are ignored.
This addiction to drama seems to undermine efforts to implement processes such as Embedded Quality that help projects run smoothly. Personally, I prefer to keep drama in the movies and out of my projects.
Overcoming Addiction
Is there any way to supply teams with the excitement and adrenalin rush associated with the visible, novel, and dramatic while still implementing processes and procedures that keep things running smoothly? It’s definitely a challenge, but there are some techniques that can help.
Celebrate Success
When a project goes smoothly because talented, dedicated people adhered to a good process, make that success visible. Celebrate the success publically and enthusiastically, and point out that the reasons for the success.

Create Positive Challenges
Talented, dedicated people crave novel challenges, so it’s important to provide productive challenges so people don’t fall back on the challenges of heroic efforts. The challenge might be to improve on the success of a previous project or it might be to learn a new skill, technical or otherwise. Any extra time or risk invested in team members learning a new skill on a project will pay dividends in employee motivation and skillset in the future.
Don’t Reward Unnecessary Drama
If a team is forced to work ridiculous hours to save a project due to failure to follow a process, thank people for their efforts and point out how the drama should have been avoided. Don’t celebrate the efforts as something to be emulated in the future.
You do need to be careful to determine the true cause of the drama, though. Every project can’t be perfect, and you do want to reward heroic efforts when they’re truly justified.
Feedback
I’m interested in hearing about other ideas for keeping teams enthusiastic and motivated when processes are running smoothly and efficiently. I’d love to hear about any techniques that you’ve tried and how they turned out.
When the Firefighter is the Arsonist – Tales from the Trek
- November 3, 2016
- Kevin Rutkowski
- Comments Off on When the Firefighter is the Arsonist – Tales from the Trek
A number of years ago, I read a headline that said, “Ex-Forest Lake fire fighter pleads guilty to arson“. The story went on to say,
“Once considered a hero as a firefighter, John Berken was accused of starting a fire that burned 2,000 acres of nature area.”
This story got me thinking about a common pattern that I have seen on software development projects.
Heroic Measures
Many teams glorify the team members who take heroic actions to save a project. These team members, who work nights and weekends for weeks, or even months, at a time to pull a project success from the jaws of defeat, are held up as positive examples for the company and lavished with praise.
However, too often, the very same people who perform the heroic deeds are the people who created the near-disaster in the first place.

As a QA Sherpa, one of my top goals is to prevent the need for heroic actions at the end of a project. I feel happiest when we successfully implemented Embedded Quality and find no important bugs during the last few weeks before going live. In this role, I’m particularly attuned to those “heroes” who actually created the problems in the first place.
These are the people who dramatically underestimated their work, skipped unit testing, refused to work with the testing team to practice Embedded Quality, and generally eschew any form of teamwork or foresight. Despite all these negative traits, they end up being celebrated for “going above and beyond the call of duty”.
True Firefighters
True firefighters do need to be heroic at times, and it’s important that they are ready and able to be heroes when necessary. However, their bigger goal is to prevent fires in the first place. In addition to preventing fires, they work hard to put measures in place to limit the damage of fires when they do occur.
The bulk of a fire department’s efforts are not spent putting out fires. The bulk of the time is spent educating people about how to prevent fires, ensuring that the fire code is effective and that buildings follow the fire code by implementing fire walls, fire doors, sprinkler systems, alarms, and fire extinguishers.

Similarly, a solid development team should be spending their time implementing automated unit testing, working with the test team to implement Embedded Quality, performing peer code reviews, and getting feedback from key stakeholders throughout the project. All of these actions work both to reduce the odds of a disaster and to limit the damage when a disaster occurs.
As I said earlier, heroes are still needed at times, but you should take a second look at those heroes when the disasters are too frequent. If a city has way more fires than the norm, the fire department probably isn’t doing their job well. If every project requires heroic measures, it’s time to look a little closer at why that’s the case.
Feedback
I’m interested in hearing about your experiences with fire fighters who may also be arsonists. Have you worked on a project where team members who seemed to sabotage the project early on were held up as heroes at the end of the project? If so, do you think it was due to the individuals on the project or due to a broken system?
Influencers – James Bach
- September 15, 2016
- Kevin Rutkowski
- Comments Off on Influencers – James Bach
There are a number of blogs that I enjoy reading about all areas of the software development process. The software development process includes project management, business analysis, development, and testing, of course. In addition, delivering software that works requires consideration of concepts around management, sales, and business organization.
I’d like to share some of the blogs that I find influential when thinking about how to build software that works.
James Bach and Exploratory Testing
One of my favorite blogs is James Bach’s Blog. He is the creator of Rapid Software Testing. I first became interested in his blog because he wrote about exploratory testing in a way that made sense to me. I knew from experience that exploratory testing was one of the best ways to find important bugs, but I didn’t have a great way to communicate the high value of exploratory testing to teams that were focused heavily on mechanizing the testing process. James Bach has written a lot on the topic of exploratory testing. This particular post about the history of Exploratory Testing captures many of the concepts that drew me to the blog.
I particularly like the concepts of testing vs checking and the “responsible tester.”

Feedback
What do you think of James Bach’s blog and the concepts he writes about? What blogs and resources do you find particularly interesting and useful for building software that works?
Embedded Quality – Building on a Solid Foundation
- August 24, 2016
- Kevin Rutkowski
- 1 Comment
Embedded Quality is a Quality Assurance (QA) technique that I’ve introduced on many projects with great success. Embedded Quality has some of the following benefits:
- Avoids long test/fix cycles at the end of projects
- Ensures that projects finish strong
- Lowers cost
- Shortens timeline
- Improves quality
- Increases customer confidence in IT department
- Easily applied to any software development methodology
Basic Concepts
The basic concepts of Embedded Quality are nothing Earth-shattering. The concepts draw from standard software development techniques and seem like they should be common sense. However, in the 20+ years that I’ve been working in software development, I’ve found that these concepts are not commonly practiced.
QA starts on Day 1
I have found that on many projects, Quality Assurance is an after-thought. Involving QA as part of the core project team helps prevent nasty surprises at the end of the project.
QA is part of the Core Project Team
Too often, the development team and QA team are completely separate entities who send their work “over the wall” to each other. Quality and speed increase exponentially when we break down the barriers between these groups and work as a team.
QA is performed by qualified experts
One of my clients used to hire people out of high school to test their software. If they did well, they got promoted to doing phone support. Eventually, they realized that they could drastically decrease phone support and increase customer satisfaction by hiring qualified people to do their Quality Assurance work.
Just as building inspectors need special knowledge and experience to do their jobs well, software QA experts need special knowledge and experience to do their jobs well.
General User Acceptance Testing (UAT) does not begin until Core Project Team QA is complete
A common practice on projects is to rely on UAT as the only form of testing. This results in the end users seeing a large number of the flaws in the software. Invariably, I have seen the end users permanently lose confidence in the development team when using this QA strategy.
I liken this to a builder turning over a new house to a buyer without having any inspections and saying, “We don’t really know if the plumbing is solid, all the electricity works, or the roof leaks. Just try everything out and let us know what the problems are.” (In fact, this does happen: http://abcnews.go.com/GMA/Consumer/story?id=2630414&page=1.)
Strong Foundation – No code is “Complete” until it is tested and works correctly
Many project schedules track code as complete when the developer completes their initial delivery. This can give a false impression of the project status.
More importantly, this ensures that new code is built on a strong foundation. When developers build new code on untested code, it is very similar to building an office tower on a foundation that has not been inspected. If a problem exists in the foundation and is not identified early, the building will fail.
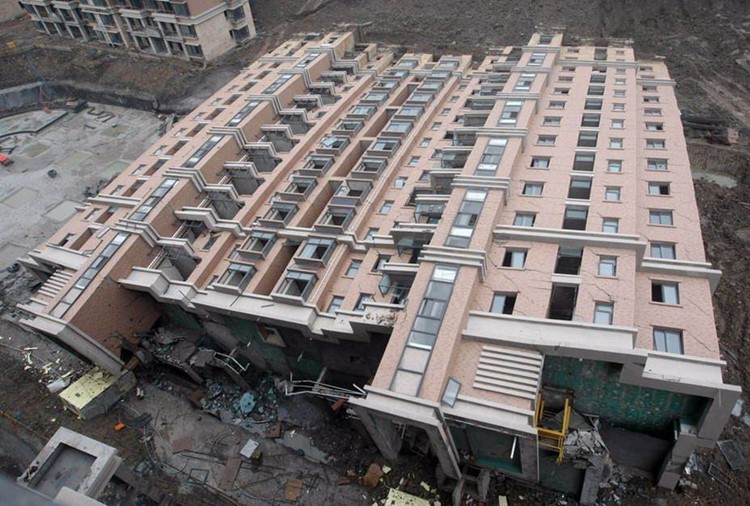

http://blogs.wsj.com/chinarealtime/2009/06/29/shanghai-building-collapses-nearly-intact/
Embedded Quality – Next Steps
Over the next few months, I will post tips on how to implement Embedded Quality on your next project. I’ll share stories of my experiences over the past 20+ years, and I would like to hear your experiences as well.
